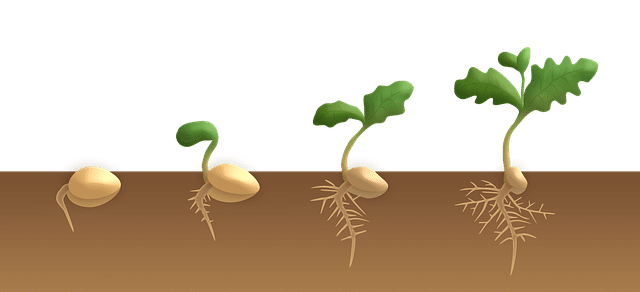
What is the Germination of seed?
Germination of seed is simply the process of the development of the seed embryo into a seedling.
There are basically two types of germination – the hypogeal and the epigeal form of germination.
Reasons your seeds don’t germinate
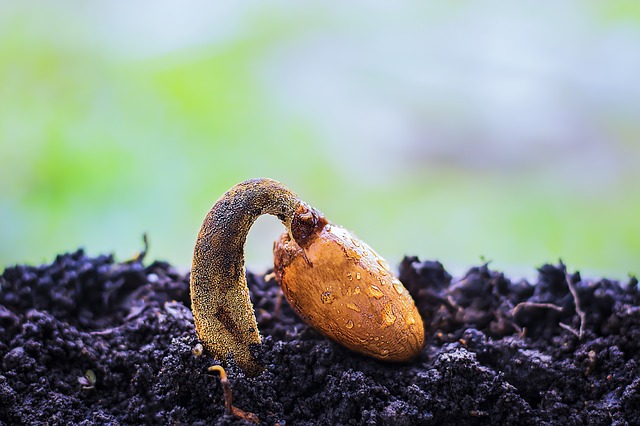

Seeds face great dangers before they can germinate into seedlings.
Besides poor practices like seeds not being stored properly, seeds are old, the seed is planted too deep, etc which can be the reason seeds are not germinating, there are other natural factors.
Seeds are often destroyed by excessive heat or cold, or by animals that feed on them and crush them to useless bits.
If seeds that normally grow in rather dry soil should be any chance fall into the sea, rivers, or ponds, they may not be able to germinate and grow into seedlings because of unsuitable conditions.
The condition necessary for Seed Germination
There are different factors affecting seed germination, some are natural while others are human practices.
Some of the external conditions necessary for germination are water, air, and a suitable temperature while the internal conditions are enzymes, energy, and the viability of the seed.
The necessity of the external conditions is easily demonstrated through experiments, while that of the internal conditions is not.
However, the most important factors affecting seed germination are water, oxygen, and a favorable temperature.
These are the three things seeds need to germinate.
- Water softens the seed coat and also dissolves the soil nutrients
- Oxygen is important to break down food stores in the seed and to produce energy for germination.
- Every seed needs a certain level of temperature for germination, so an optimum temperature is important for seed germination.
It is quite clear that seeds need these conditions to germinate and grow. else, the seeds will remain dormant in the soil.
The Importance of Water in Seed Germination
A non-germinating seed contains very little water. However, for the initiation of germination, it needs excess water to activate its cell.
Therefore, a seed absorbs a large amount of water through its micropyle.
In many cases, water can also enter through the seed coat, which is porous.
The protoplasm, when saturated with water, becomes active.
The absorbed water also activates the enzymes in the cells and dissolves the stored food.
Water is the medium in which all chemical and enzymic reactions proceed.
Water is also the medium of transport of dissolved food substances through the various cells to the growing regions of the radicle and plumule.
Besides, water softens the seed coat which can consequently of the radicle and plumule
The Importance of Air in Seed Germination
All living cells need the energy to activate their protoplasm for cell division and growth.
This energy is obtained by the oxidation of food substances stored in the seed through respiration.
Oxygen is necessary for respiration, therefore, the air is another important factor that is necessary for germination.
Seeds buried deep in the soil do not germinate due to lack of air.
They also fail to germinate in wet or waterlogged soil which is usually very poorly aerated.
Seeds are placed in water that has been previously boiled and the water has lost most of its air content through boiling.
The Importance of Temperature in Seed Germination
Most seeds require a suitable temperature range for germination.
Seeds will not germinate at temperatures below 0°c or above 45°c.
The best range of temperature or the optimum temperature range for germination is between 28 to 37.
At higher temperatures, the protoplasm and enzymes of the cells are destroyed, while at very low temperatures, they become inactive.
Therefore, the protoplasm and enzymes function with temperature until it reaches a maximum value at the best, zero optimum, temperature, thus varies from one plant to another.
The Importance of Enzymes in Seed Germination
Many important activities such as respiration and the utilization of food substances can not go on without the help of enzymes.
Respiration requires a series of enzymes.
Carbohydrates are usually stored in seeds in the form of insoluble starch.
The latter has to be made soluble before it can be used by the developing embryo.
Similarly, fats and proteins, which are present in most seeds, have to be broken down into simple molecules.
All these reactions occur by hydrolysis and are catalyzed by enzymes such as diastase (for carbohydrates), lipase (for fats), and protease (for protein).
Enzymes are also necessary for the conversion of some of the hydrolyzed products to new plant tissues.
The Importance of Energy in Seed Germination
If life is to go on and cells are to perform all their activities, energy must be available.
In germinating seeds, a large supply of energy is essential for maintaining the activities of the rapidly developing and growing embryo.
Energy is obtained from food stored in the endosperm or cotyledons of a seed.
The Importance of Seed Viability in Seed Germination
Only seeds that have life and are healthy will be able to germinate and grow.
Many seeds that have been stored for several years may have lost their viability.
As a result, germination will not occur in these seeds.
However, there are seeds that can survive for several years provided that they are properly stored and not damaged by rodents, insects, or fungi.