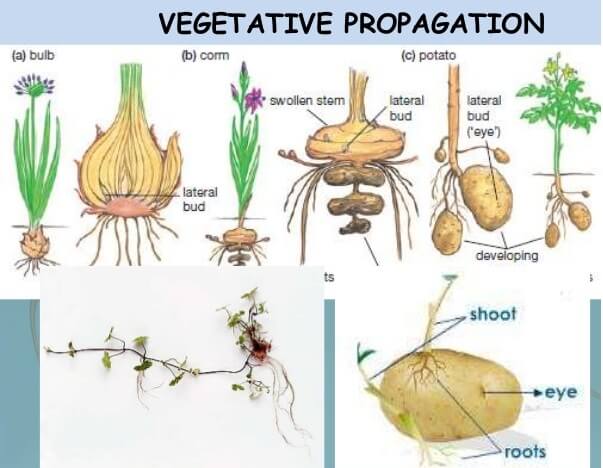
What is Vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is an asexual means of reproduction in plants, whereby gametic cells are not involved in this process.
Vegetative propagation occurs when a new plant grows from any portion of an old one other than the seeds.
In other words, the new plant is produced from a vegetative part of the parent plant.
Types of Vegetative propagation
There are two types of Vegetative propagation – Natural and Artificial vegetative propagation.
If part of a plant is to be used to produce a whole new plant, that part must be able to produce all the organs, both vegetative and reproductive, of a complete plant, namely, roots, stems, leaves, and flowers.
Methods of Vegetative propagation
There are tens of methods used in Vegetative propagation.
For natural Vegetative propagation in a plant, creeping stems, underground stems and shoots, cors, stem tubers, bulbs, adventitious bulbs, bulbils, and root tubers.
For artificial vegetative propagation, the methods are cuttings, marcotting, layering, grafting, bud grafting, and stem grafting.
Organs of Vegetative propagation
If the part used for vegetative propagation is a stem, the stem must be able to grow roots and leafy stems.
if the part used is a root, it must be able to develop more roots as well as buds which will produce flowers and leafy stems.
Both the stems and roots of certain plants can reproduce vegetatively.
In certain cases, vegetative propagation can occur through leaves that are capable of producing tiny new plants called plantlets.
In the case of reproduction by seeds, the reproductive organs of a plant are indispensable as seeds are produced from them.
Both organs of vegetative propagation and seeds are similar in one respect -They have a store of food that can be supplied to the new plant and can sustain it until it is capable of manufacturing food for itself.
However, there is one point of difference – most new plants arising from seeds, that is, seedlings, are independent of the parent plants while many new plants produced vegetatively are not.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vegetative propagation in Plant
Both natural vegetative propagation and artificial vegetative propagation have their advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Growth in vegetative propagation is rapid and easier compared to plant propagation by seeds.
- It helps in the preservation of plant properties since only one parent plant is involved in reproduction.
- Plant’s offsprings are not wasted unlike sexually propagated plants
- Much energy is not required in vegetative propagation compared to seed propagation
Disadvantages
- New varieties or hybrids can not be produced from this method
- Diseases can easily be transferred to the new plants from the parent plants
- There’s very little chance of dispersal, hence, competition among the new plants.
- Vegetative propagation leads to overcrowding around the parent plants, this is evident on plantain farms.