What is a flowering plant?
Flowering plants are plants with well-developed reproductive parts, and capable of producing flowers, fruits, and seeds.
Flowering plants are also regarded as angiosperm.
The flowering plants show great variety and diversity of form.
However, they carry on the same basic activities, and despite their seeming diversity, they exhibit a great similarity in their structure.
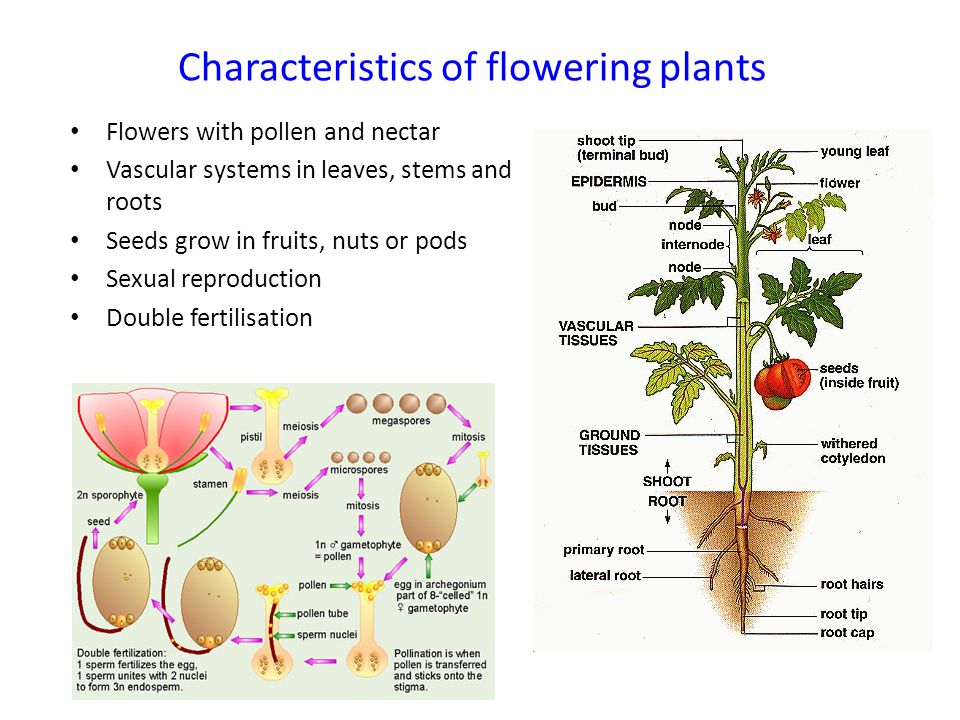
Characteristics of Flowering Plants
All the activities of the different parts of the plant are so coordinated that the plant can live, grow, and reproduce as a unit.
A typical flowering plant consists of vegetative and reproductive organs. the vegetative and the reproductive organs.
The vegetative organs are the roots, stem, and leaves, while the reproductive organs are the flowers, which are concerned with the production of fruits and seeds.
Types of Flowering Plants
There are two types of flowering plants – Liliopsida and Magnoliopsida.
The former is commonly called monocotyledon while the latter is a dicotyledon.
Classification of Flowering Plants
While flowering plants are of 2 types, they can be broadly categorized into 3 groups based on the nature of their life cycle and their span of life.
The 3 classes of flowering plants are Annuals, Biennials, and Perennials.
-
Annuals
An annual is a plant that completes its entire life cycle and dies within one growing season which may be a few months or at the most one year.
After the seed germinates, the plant grows and produces flowers which in turn produce fruits and seeds.
Once the seeds have been produced, the rest of the plant dies.
Many of the world’s most useful plants are annuals.
Examples of annuals include cereal plants like rice, wheat, maize, bean and pea plants, flax, jute, okra, and sunflower.
-
Biennials
A biennial is a plant that passes through two different phases in one life cycle.
In general, it has a longer life span than an annual, the life span is approximately two years, that is a year for each phase.
During the first phase, biennials such as the carrot attain their full vegetative growth and develop large storage organs.
Food stored in these organs is made use of in the second phase when the plant sends up a left shoot bearing flowers, fruits, and seeds. After this, the plant dies.
If adverse conditions prevail after the first phase, the vegetative shoot dies down.
When favorable conditions return, the storage organs produce new vegetative shoots.
Many garden food plants are common examples of biennials, for example, radish, cabbage, and turnip.
Usually, these plants are harvested for food immediately after they complete their first phase of growth.
-
Perennials
Perennials are trees, shrubs, and herbs which continue to grow from year to year, producing flowers, fruits, and seeds for many years.
They can be divided into two groups – herbaceous perennials, the aerial parts of the plants may die down every year at the end of the favorable reason after producing flowers and seeds.
Most herbaceous perennials persist using underground stems and roots, for example, corns, bulbs, tubers, and rhizomes.
These usually contain a store of food that is used for the production of new flowering shoots when the favorable season returns.
Usually, the terminal or later (axillary) buds on these underground organs develop to form new aerial shoots.
Examples of herbaceous perennials are lilies, dahlia, water-chestnut, onion, garlic, and ginger.
Woody perennials are plants such as trees, shrubs, and vines, in which the aerial stems and branches persist and grow from year to year.
Trees growing in temperate countries shed leaves with the approach of winter and are said to be deciduous.
Some trees in the tropics also behave similarly, However, most trees growing in the tropic never shed all their leaves at the same time and are said to be evergreen.
Examples of woody perennials are the flamboyant (a deciduous tree) and the Bougainvillea (an evergreen shrub)